Image optimisation is an essential aspect of marketing that helps businesses enhance their online presence and increase their website traffic, and unfortunately, it is often forgotten. Optimising images involves the image format and reducing their file size without sacrificing quality to ensure they load quickly and efficiently on websites, emails, and social media platforms. This not only improves the user experience but also has a positive impact on your image search results and engine rankings. Additionally, well-optimised images can boost engagement levels and lead to increased conversions. Something we all love to hear, right?
Businesses must prioritise image optimisation as part of their overall marketing strategy to ensure that their brand stands out in today’s over-saturated digital landscape.
Why Is SEO for Images Important?
Google’s search engine ranking algorithm is complicated and SEO is essential for any website that wants to rank well in search engine results pages. When it comes to images, optimising them for search engines can greatly improve a website’s visibility and attract more traffic. This is because search engines use various factors, including image file names, alt tags, image tags, and surrounding text, to determine the relevance and quality of an image. By optimising these various image and alt tag elements with relevant keywords and descriptive phrases, website owners can help search engines better understand the context and content of their images, making them more likely to appear in relevant search results. Properly optimised images can also improve the user experience, as they can load faster and be more accessible to users with disabilities or slow internet connections.
Images Give Context to Your Content
Images are essential to any content, as they provide visual context to the information being presented. A well-chosen image can communicate a message quickly and effectively, helping to engage the reader and enhance their understanding of the text. An image of a graph or chart can help to explain complex data, while a photograph can add emotion to a story and bring it to life. Images also serve to break up text blocks, making content more visually appealing and easier to digest. In today’s digital age, where attention spans are short and competition for engagement with visual content is high, including images is crucial for creating content that stands out and resonates with the audience.
Using Alt Text for SEO
Alt text, or alternative text, is a brief description of an image that is included in the HTML code of an image belonging to a webpage. This text is used by readers to describe the image to visually impaired users and can also be displayed in place of the image if it cannot be loaded. Alt text plays an important role in image optimisation by providing context to search engines about the content of the image. By including relevant keywords in the alt text, marketers can help search engines better understand the relevance of the image to the content of the webpage. This can improve the web page’s overall SEO and help it rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant searches. However, it’s important to avoid keyword stuffing in the image alt tags and text and to ensure that the description accurately reflects the content of the image to provide a good user experience.
How To Optimise Your Images for SEO
1. Choose the Right File Format
The most common image formats for the web are JPEG, PNG, and GIF. JPEGs are great for photographs, PNGs are better for images with transparent backgrounds, and GIFs are suitable for simple graphics and animations.
2. Resize the Image
Resize the image to the appropriate dimensions for your website, as large images can slow down page speed on your website. You can use image editing software like Photoshop or GIMP to resize your images.
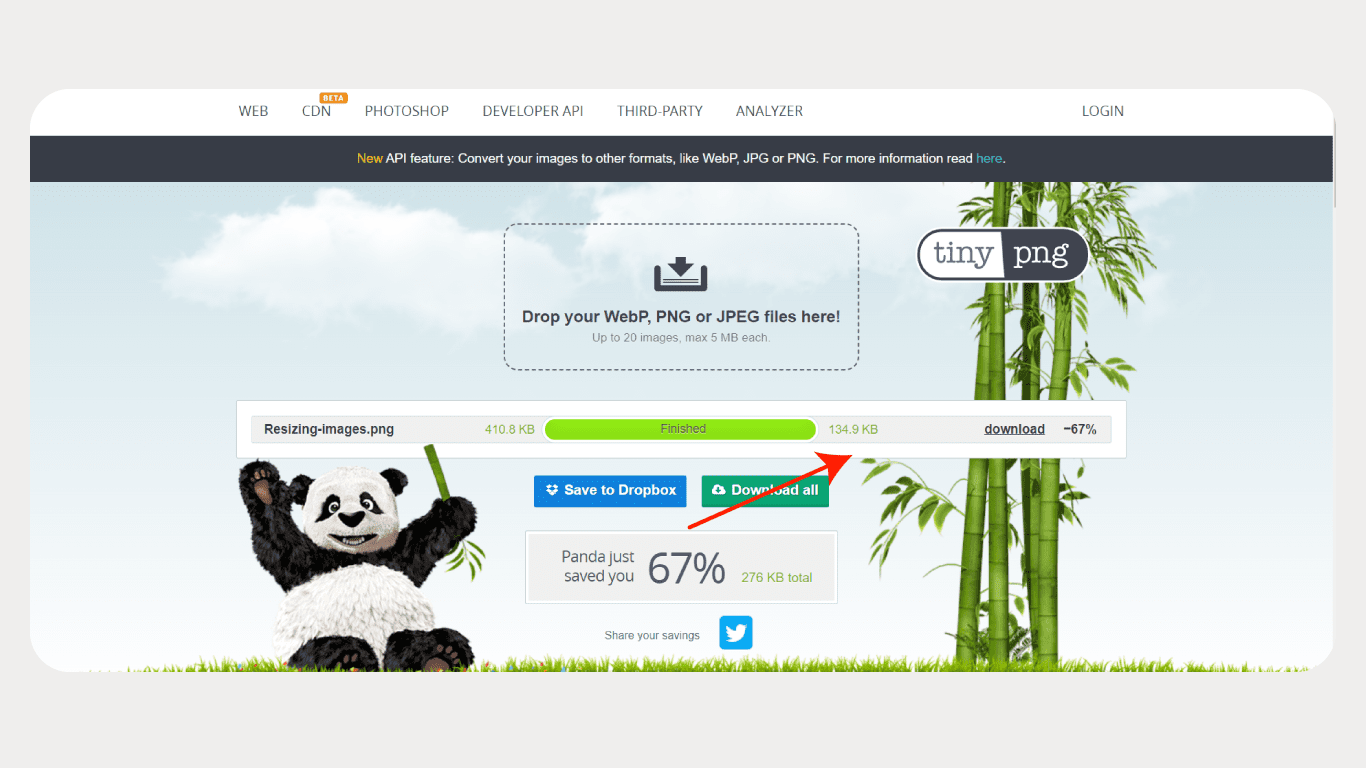
3. Compress Images for Faster Load Time
Compressing images is an important step in optimising image size for web pages and reducing their loading time. Images with large file sizes can significantly slow down a website’s performance, resulting in a poor user experience. By compressing images, you can reduce their file size while maintaining their visual quality. This helps to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred from Google images from the server to the user’s device, resulting in faster load times and a smoother browsing experience. You can use image compression tools like TinyPNG, JPEG Optimizer, or Compressor.io to compress your images.
4. Use Responsive Images
Using responsive images can have a positive impact on web pages and SEO because it can improve the user experience and the web page loading speed on mobile devices, which are factors that search engines take into account when ranking websites.
Responsive images are images that adjust in size and resolution based on the screen size of the device they are being viewed on. This means that the images will load quickly and display properly on any device, whether it’s a desktop computer, tablet, or smartphone. Search engines, such as Google, place a high value on user experience, and fast-loading websites that are optimised for mobile devices are more likely to rank higher in search results. They can also reduce bounce rates and increase engagement, which can further improve SEO.
5. Customise Image File Names
Rename your image files with descriptive and relevant file names that accurately reflect the image’s content.
Let’s say you have a picture of a beautiful sunset on a beach that you want to upload to your website. Instead of naming the file something generic like “IMG1234.jpg,” you can customize the file name to be more descriptive and SEO-friendly.
For example, you could name the file “sunset-beach-ocean-view.jpg.” By including relevant keywords in the file name, you make it easier for search engines to understand what the image is about and index it accordingly. This increases the likelihood that your image will appear in search results for relevant queries, which can help drive more traffic to your website.
6. Write SEO-Friendly Alt Text
To write alt text, you should describe the image accurately and concisely, using relevant and specific keywords. Avoid using phrases like “image of” or “picture of” and instead describe the image’s content, context, and function. Alt text for Google images should be brief and to the point, but descriptive enough to convey the image’s purpose and meaning. Keep in mind that alt text is primarily for screen readers and users with visual impairments, so prioritize clarity and accuracy in writing your image alt text over creativity and aesthetics. With proper alt text, your website can become more inclusive and user-friendly for everyone.
Here’s an example:
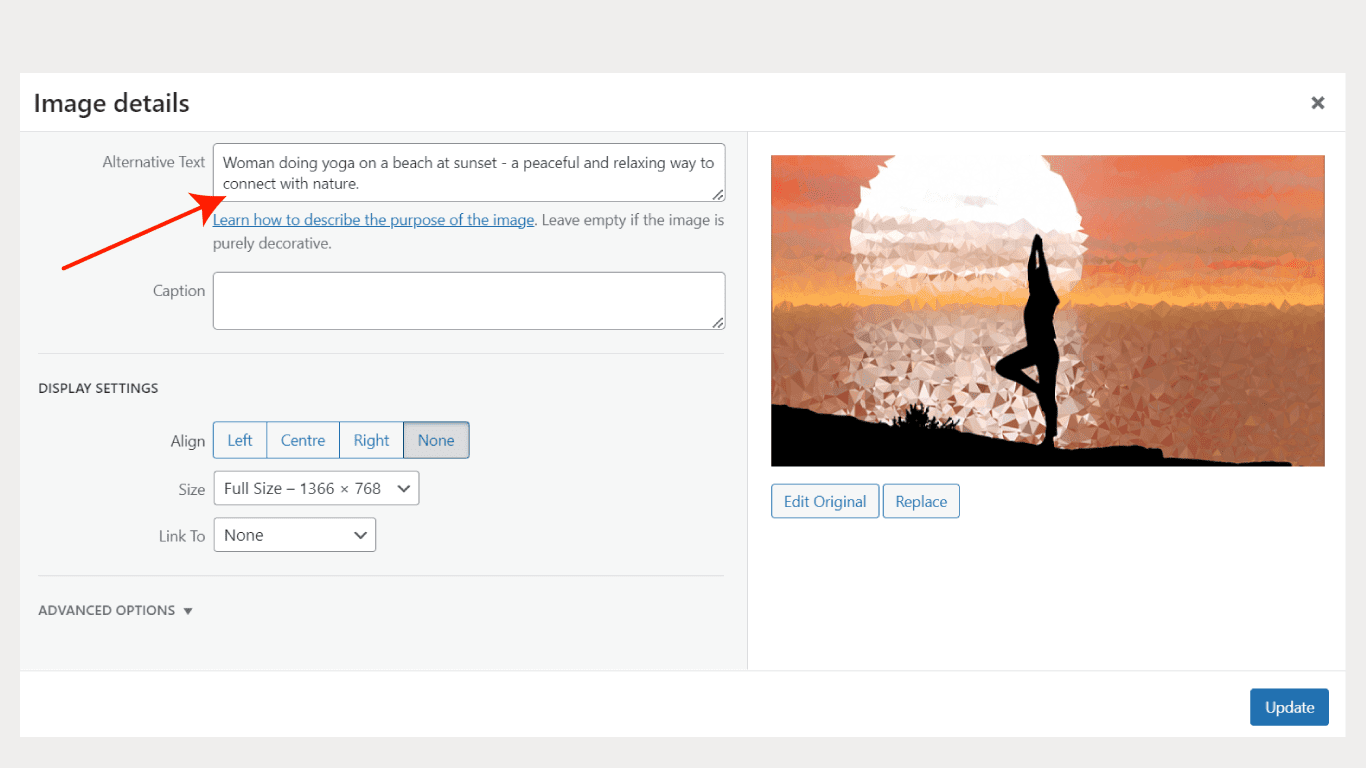
Image: A woman doing yoga on a beach at sunset.
Alt Text: “Woman doing yoga on a beach at sunset – a peaceful and relaxing way to connect with nature.”
In this example, the alt text accurately describes the image, including relevant keywords such as “yoga” and “beach.” It also adds some additional context to the Google image search, which could help it appear in search results for related terms such as “nature yoga” or “relaxation on the beach.
Some other key factors
EXIF Data
EXIF data is information that is stored in digital image files and provides details about the camera or device used to take the photo. It includes information such as the make and model of the camera, shutter speed, aperture, ISO, focal length, date and time the photo was taken, and location if the device has GPS capabilities. EXIF data can be accessed using image editing software or online tools and can provide valuable information for photographers.
It can be important to add images for SEO because it provides additional context about the images on your website, making them more easily indexable and understandable by search engines. By including relevant keywords in the image file name and the EXIF data, you can help search engines better understand the content of the image and improve its visibility in search results. Additionally, EXIF data can help improve user experience by providing information about the quality of the image, such as the resolution, aperture, and shutter speed. This information can be useful for users who are looking for high-quality images and can help to reduce bounce rates on your website. Overall, including EXIF data can be a valuable tool for improving the SEO of your website’s images and enhancing the user experience.
Next Gen file type
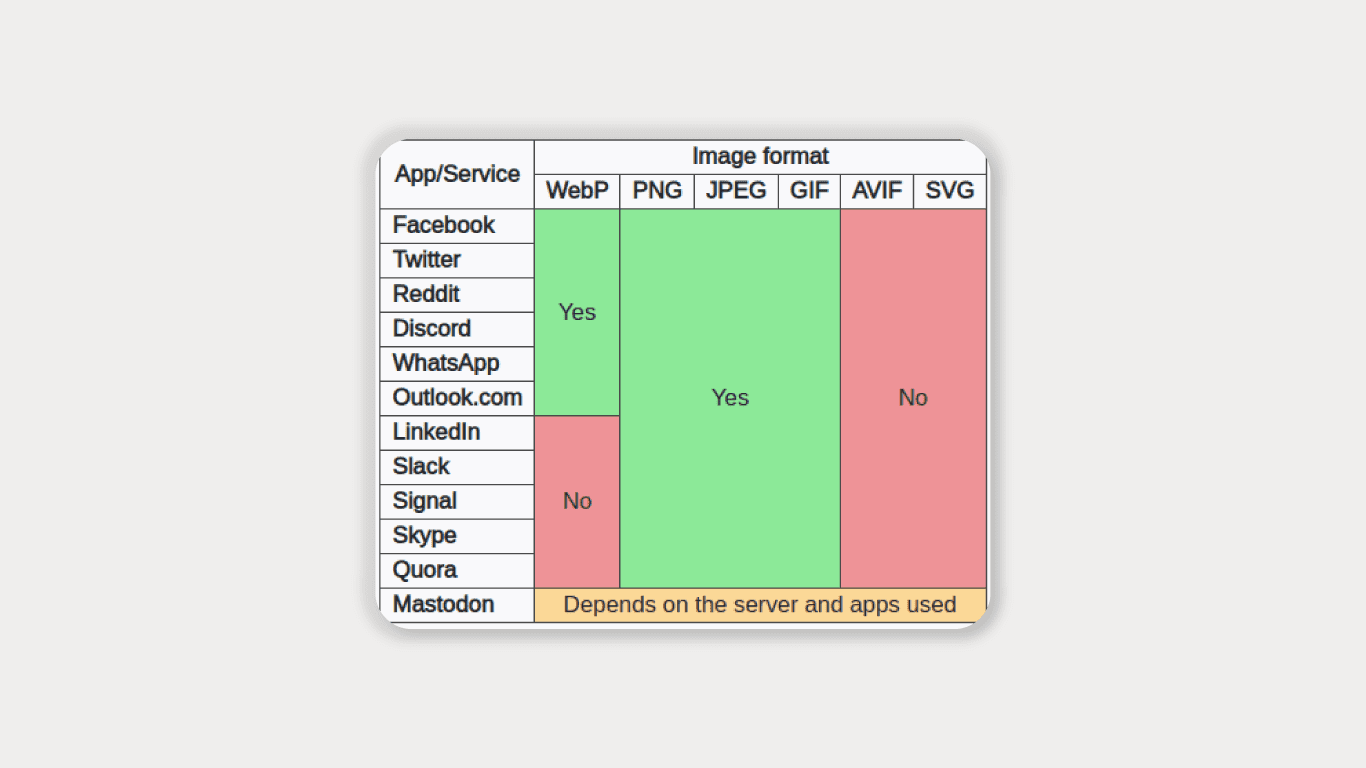
Next Gen file type refers to a new kind of image format that is better than traditional formats like JPEG and PNG. They use advanced compression algorithms to make smaller file sizes without making the image quality worse. Examples of Next Gen file types include WebP, JPEG, and AVIF. Next Gen file types are popular because they help websites load faster, use less internet data, and make the user experience better.
However, not all devices and internet browsers can view Next Gen file types, so it’s important to have a backup plan like using alternative formats for users who cannot see them. Next Gen file types can help improve website speed by reducing the file size of images while maintaining a high-quality image itself, which also results in faster load times and a better user experience. Additionally, using Next Gen file types can help reduce bandwidth usage, which can be particularly important for users who have limited data plans or are located in areas with slow internet speeds.
Next-generation image formats:
- AVIF (AV1 Image File Format) – Developed by the Alliance for Open Media, AVIF is a modern image format that offers high image quality at low file sizes, suitable for the web.
- WebP – Developed by Google, WebP is another modern image format that provides both lossy and lossless compression, making it an excellent option for web use.
- HEIF (High-Efficiency Image Format) – Created by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG), HEIF is an image format that offers advanced compression and storage capabilities, supporting both single images and image sequences.
Historical image formats used on the internet:
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) – Introduced in 1987, GIF became popular on the internet for its ability to support simple animations, transparency, and interlacing. However, it is limited to 256 colours, making it less suitable for high-quality images.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) – Developed in the early 1990s, JPEG is a widely used image format on the internet that supports lossy compression, allowing for smaller file sizes but with a reduction in image quality.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics) – Introduced in the mid-1990s as a replacement for GIF, PNG is a lossless image format that supports a higher colour depth and transparency, making it a popular choice for images on the web.
- BMP (Bitmap) – Developed in the 1980s, BMP is a lossless image format that was once used on the internet, but its large file sizes have made it less popular over time.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) – Created in the mid-1980s, TIFF is a flexible and powerful image format that has been used on the internet, but its large file sizes and complexity have limited its popularity for web use.
| Image Format | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVIF | High image quality, low file sizes, modern compression | Limited browser support | Web images, high-quality photography |
| WebP | Lossy and lossless compression, smaller file sizes | Not universally supported | Web images, responsive designs |
| HEIF | Advanced compression, storage capabilities, image sequences | Limited browser support, patent/licensing issues | Photography, image sequences |
| GIF | Supports animation, transparency, interlacing | Limited colour depth, less efficient compression | Simple animations, icons |
| JPEG | Widely supported, small file sizes, adjustable compression | Lossy compression, no transparency support | Photography, web images |
| PNG | Lossless compression, high colour depth, transparency | Larger file sizes compared to JPEG/WebP/AVIF | Web images, icons, logos |
| BMP | Lossless compression, simplicity | Large file sizes, limited features | Rarely used, simple graphics |
| TIFF | Flexibility, powerful features | Large file sizes, complexity, limited web use | Desktop publishing, high-resolution images |
Image Optimization Summary
Optimizing images for SEO is an important aspect of digital marketing that can have a significant impact on website traffic and search engine rankings. Best practices for image SEO include compressing image files, using descriptive file names and alt text, adding relevant keywords to image titles and metadata, using Next Gen file types where possible, and optimizing image dimensions and placement.
By following these steps, website owners can improve website speed, enhance user experience, and make it easier for search engines to understand the content and purpose of images on their websites. Incorporating image SEO into your digital marketing strategy can help boost website visibility, increase traffic, and ultimately drive business growth. A win-win situation for both website owners and visitors!














Leave a Comment