In the past, optimizing your website to improve user experience was a nice perk. But as Google continues to update its search engine algorithm to determine search ranking positions for websites, site owners must adapt to it.
If you don’t, your organic traffic will go down, pushing your website farther into the search results for a relevant keyword.
However, SEO can be easily overwhelming. It is believed there are up to 200 ranking factors for Google. It can easily overwhelm marketing managers, especially if you are trying to make it to the first page for your target keywords.
One of the critical ranking factors to pay attention to is page experience, or user experience (UX). It matters – for real now. And if you don’t prioritise page experience, it negatively impacts your Google search results performance and could leave your website users dissatisfied.
Let’s dive closer into the impact of page experience on your Google search performance and how to utilise that to your advantage.
Insights to the Web Vitals Update
In May 2020, Google announced its plans for the Web Vitals update. The new algorithm update results from extensive research on the most important metrics directly related to the site user’s experience. Within this set of metrics are sub-metrics known as Core Web Vitals.
Google claims these updates will focus on “real-world, user-centred metrics” that quantify the overall page experience. It will evolve over time, just as any other element involved in Google search results ranking. However, the initial rollout of the Web Vitals update focuses on 1) loading, 2) interactivity, and 3) visual stability.
Google fully implemented the new algorithm update in 2021. The update was evident in how Google displays results for a particular Google search, such as the Featured Snippets and the Top Stories section. The Web Vitals update aligns with Google’s renewed focus on moving away from traditional on-page SEO strategies (keyword density and meta description) and toward advanced strategies, including the web page user experience.
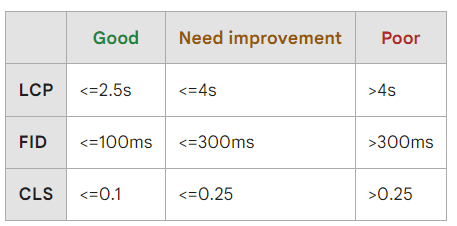
As mentioned, Google’s new update introduced a sub-metrics for Google ranking called Core Web Vitals. The three-page performance-oriented metrics are LCP, CLS, and FID.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
This metric indicates how long it takes for the largest content element in a web page to load or become visible to the web user. The term “largest” refers to the space utilized in the screen area and the weight of the data required to load that content.
For example, if you are reading an article, the LCP for that page would most likely be the featured image or a video since they are heavier and takes longer to load than lightweight elements like web page text.
So, how do you know if your LCP is good? According to Google, the LCP must load within 2.5 seconds. Your website needs improvement if the LCP loads between 2.5 to 4 seconds. And if it takes more than 4 seconds, that would mean a poor page experience for the users.
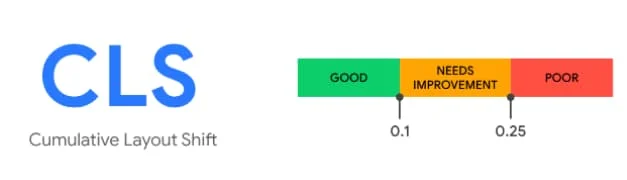
Cumulative Layout Shirt (CLS)
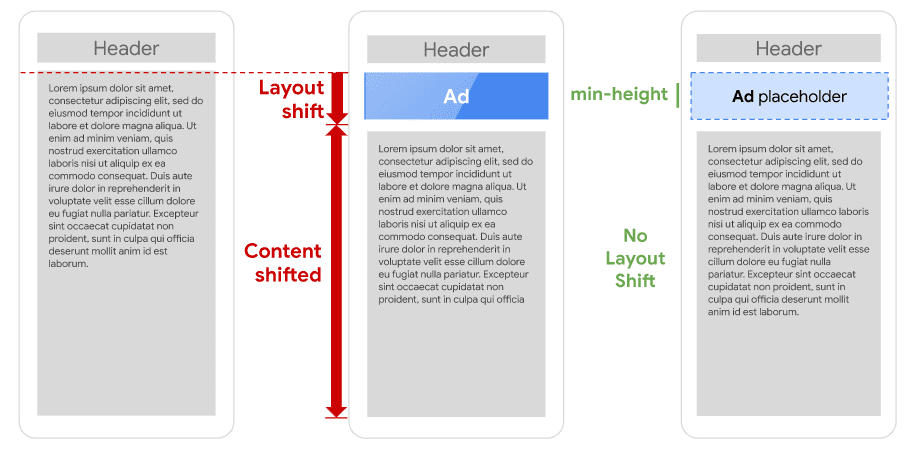
This metric measures the visual stability of the web page. This Google ranking factor greatly affects the user experience because you don’t want the page elements to move around while using it. This metric quantifies the frequency of the layout shifts while browsing a page, especially if you are trying to execute certain actions like clicking a button or navigating to other pages.
One of the main culprits for the page elements shifting around would be the unknown dimensions of images and videos. It could also happen due to the different types of fonts used in a website or the presence of in-content ads. Most website owners would want to avoid using dynamic web page elements since they can result in them shifting around as the page loads.
Scoring the CLS can be more difficult to measure than the LCP. However, website owners must aim for a CLS score of 0.1. Anything higher than that could result in a poor web user experience.
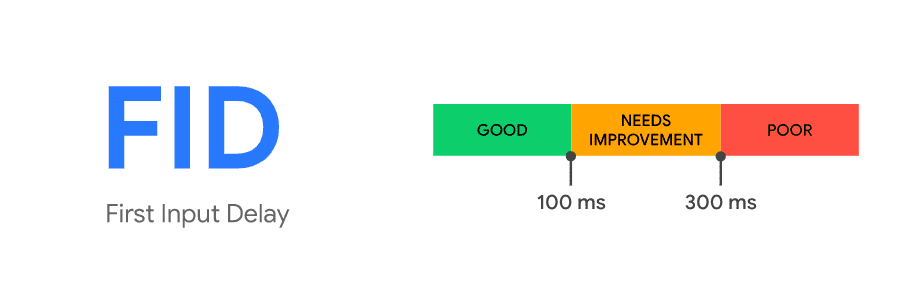
First Input Delay (FID)
This metric assesses how long it takes for a website to execute the first command initiated by the user. For example, you click a button to go to another page. Some websites take a while to load to a new page because it is still “busy” loading other page elements from the previous page.
Google prioritises websites that are highly responsive and interactive. Therefore, you must aim to improve the input responsiveness of web pages by eliminating delays in executing page actions for a particular site.
A good FID score for web pages would be less than 100 milliseconds. This rate ensures that the web page is ready to respond to the action that the user wants to initiate. It is critical for ecommerce websites because any delays could lead to the user abandoning their carts – and a missed sale opportunity.
Understanding the Core Web Vitals updates and its elements can be a good first step for website owners looking to optimize their ranking success. However, it’s just one of many factors that can improve Google rankings.
Page Experience as a Google Rankings Factor
Page experience is the new hot topic regarding ranking factor on Google. However, it is an umbrella term for other elements outside content quality.
For Google’s best interest, they want to improve search metrics and algorithms using a user-centric approach because it helps build more trust in the quality of search results. Any SEO expert knows the EAT philosophy: Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness. Now, you can utilize the Core Web Vitals in your on page SEO strategy to build organic traffic by reaching the first page of search results.
Mobile-First Approach
The EAT criteria for Google search results remain unchanged, but a core aspect of improving page experience is to adapt your website to deliver optimal browsing experience for users. With that in mind, optimizing your website for mobile devices can improve your on page SEO performance.
Google introduced mobile-first indexing in September 2020, which shows the importance of a mobile friendly website. Moving forward, websites must factor in the mobile user experience to boost organic search traffic.
In addition, it also requires an enhanced approach to building websites for various mobile devices. For example, you must consider the varying screen sizes with a well-coded and responsive website design. Formatting the text and other visual elements on your page is also critical in making the ranking factors work in your favour.
Secure Browsing
Website security is another critical aspect of the page experience as a Google ranking factor. Visitors expect website owners to implement safety protocols on their hosting and websites to protect users’ interests, especially for websites requiring them to share personal details and information.
A secure connection (HTTPS) is a must. In addition, it should be free from malicious content that could introduce malware or phishing software to the user’s desktop and mobile devices.
Web Accessibility
Accessibility is another key area in improving user and page experience. It is now a critical factor in determining search engine rankings, too.
Web accessibility considers various elements of a web page design that make it easy to use for people with disabilities, such as hearing and visual disabilities. Unsurprisingly, the web accessibility practices align with Google’s search engine optimization guidelines.
Currently, web accessibility is not one of the top Google ranking factors. While it won’t affect your search engine performance, it can improve the user experience. Technically, it’s difficult to measure website accessibility, but it can impact the perception of users of your website. Ultimately, they will tell others that your website isn’t functional or as useful as it should be. Google execs are saying that while it is not currently a Google ranking factor, it’s not to say that it won’t be in the future.
This website is a good example with good web accessibility features, such as high-contrast colours and images, visible links and well-organised headings.
Still, website accessibility impacts other ranking factors for search engine. For example, it can directly impact customer retention rates, bounce rates, alt text on images, and more.
Consolidating New Google Ranking Factors with Existing Ranking Factors
The rollout of the Core Web Vitals update on Google brings new challenges for web developers and website owners, especially if you want to improve Google rankings. The biggest challenge would be integrating the new Core Web Vitals updates with the existing ranking factors. Some of these Google ranking factors weigh more than others, and the order of priority is unknown. You want to focus your optimization efforts on those ranking factors that make an impact.
To help you out, the top metrics in the ranking factor for most websites using the existing algorithm include these three:
- Mobile-Friendliness – Is your website mobile friendly?
- No Intrusive Interstitials – Is your website free from nasty pop-ups?
- HTTPS – Is your website secure?
Combine the top three ranking factors above with the latest Core Web vitals update to give you a holistic picture of what search engine optimization strategy looks like if you factor in the page and user experience.
Since Google does not publish which ranking factors offer the most impact, your safest bet is to target them all and ensure that your website is optimized for these elements. It makes sense to do this since Google has enabled an approach of analysing website performance from all angles, so you need to address them to outsmart the search algorithm.
Measuring and Assessing Page Experience as Google Ranking Factor
The only way to beat the Google search algorithm is to assess your page experience and aim for major improvement continually. Make sure to consider not just the home page but the other pages, as well.
Assess the different page elements that determine search ranking performance based on Google’s new update. You can use the Core Web Vitals to measure and analyse the usability and safety of web pages, where there was none previously.
You can use your own tools to measure site speed and usability on top of the overall site performance. These tools enable you to make an informed decision on where to improve if you want to boost search engine ranking and keyword ranking for a target keyword.
Some tools available for measuring page experience include the Google Search Console. It is an easy tool you can use to assess the organic search performance of your website. It’s also a great place to see pages with poor Page Experience and instructions on improving them.
You can also run your website through page speed test tools. Again, this tool will tell you how long it takes for your page to load and how you can improve page speed performance.
You must evaluate the following questions to help determine the overall page experience for users.
- Does your website satisfy the Core Web Vitals metrics?
- Is your website secure?
- Is the website content clearly displayed on mobile devices?
- Does the web page contain any distracting scripts and ads?
- Is it easy to distinguish the different elements within the website content?
Once you have done the testing and know how well your site is doing compared to the search algorithm metrics, you can use the information in the next step to utilise these ranking factors.
Recommendations to Improve Page Experience & Your Site’s SEO
Now that you know what the Core Web Vitals update is about and how it impacts your website as one of the major ranking factors, the next step is to determine what improvements you can implement. Working on your site performance to boost search engine traffic can be technical and complicated fast.
But first, it’s worth noting that no single ranking factor guarantees you can reach the top of the Google search results. It is just one factor you can control – it’s handy that Google has provided these insights for a measurable metric.
Here are some actionable insights you can integrate into your website for improved Google rankings:
1. Speed Up the Server
Based on the Core Web Vitals update, loading times are vital to your site’s Google ranking. Focus on speeding up your server to also improve your page load times. The higher your site speed metrics, the better your Google ranking. Optimise the processes within your server to keep it from getting busy and to ensure your page loads in the shortest time possible.
There are various ways to optimize your server speed. The first step is to update your hosting plan. This is one aspect you cannot skimp on. Pick a hosting provider with good performance and reliability. Aside from updating your hosting, you must also improve your database to optimize site speed.
2. Optimize Images
Images are one of the items that can directly impact your site’s loading speed. When you want to improve Google rankings, you must start with this basic rule. Properly optimize your images to make them load quicker. It’s also a good idea to implement image SEO with your primary keyword (or other relevant keywords) and organic search engine traffic. You can also think about compressing images, using the correct resolution and size format to help them load quicker.
3. Avoid Dynamic Content
One of the new elements in the Core Web Vitals update is the CLS – cumulative layout shift. It’s one of the ranking factors that directly impact user experience. When you optimize your CLS, it won’t make your site faster – it just makes it feel faster.
It’s frustrating when users want to click on a button on your web page, but that content suddenly shifts, causing it to seem unstable. Don’t forget to add the width and height of images on your page via the CSS. It tells the server to reserve that space for an image on that site.
4. Prioritise Critical CSS to Load
When you attempt to load the page, several things are happening at once in an effort to display the page on the user’s screen. You can set the critical CSS manually or use several tools like plugins. Activating this can enhance how fast your site loads and eliminate user frustration when using your website.
5. Improve Loading of Third-Party Scripts
Ad scripts are a common example of third-party scripts that can slow down your website performance, thus affecting your site’s SEO. If your current ad provider cannot deliver decent loading times, looking at other ad providers might be a good idea.
There is also an option to host the script yourself so you can control its performance. There are other techniques to use if you want to optimize third-party scripts.
Any improvement you make with your website performance relating to the Google ranking factors is a small step in the right direction. Search engine optimization involves many moving parts, but manipulating the Google rankings factors helps you best the best site for your users.
Key Takeaways
The Google algorithm update is already out. So, if you haven’t made any major improvements to your website yet, it’s time to evaluate its performance and see where to implement those changes. The Core Web Vitals update offers measurable insights on how you can compare your website performance against real-world user experience.
Ranking success does not happen overnight. So, if you want to boost organic search traffic to your website, it’s time to look closer into the Google ranking factors t. Whether it’s a small or big change, it’s worth the try.












Leave a Comment